Notch filter
Notch filters are used in biomedical imaging for various purposes, depending on the specific application.

Application
Our customers use these filters for some of the following prupose
-
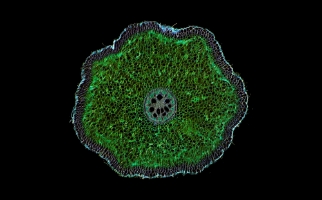
Biomedical imaging
Notch filters can be employed to block specific wavelengths associated with these artifacts or background noise while allowing the desired signal to pass.
-

Identification within biomedical samples
Isolation of specific spectral features Notch filters can isolate and capture specific spectral features or emission lines in life science samples.
-

Harmonic Generation Microscopy
In certain image processing systems that reject harmonics and interferences, Harmonic Generation Microscopy or Second Harmonic Generation (SHG) imaging processes generate signals at specific frequencies.
-

Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)
In Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) studies, the energy transfer between donor and acceptor fluorophores is measured.
-
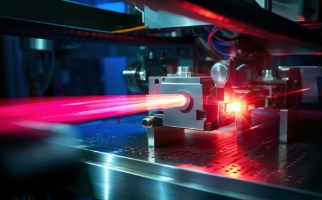
Rejection Multi-Laser Imaging System
In a rejection multi-laser imaging system, the laser lines for specific lasers can introduce unwanted signals. Notch filters are used to reject specific laser lines.
-
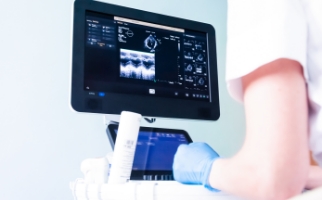
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
In optical sensors used for measurements and examinations within medical devices, filters are necessary to utilize light at specific wavelengths.
-
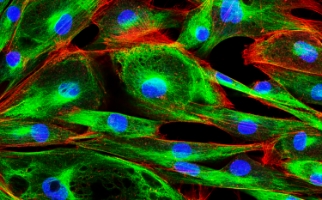
Fluorescence imaging system
In imaging systems using multiple fluorescent dyes with overlapping emission spectra, notch filters can be employed to minimize crosstalk between different channels.
-

Spectral Imaging and Hyperspectral Imaging
notch filters can be employed to selectively block specific spectral bands or lines while allowing the rest of the spectrum to be imaged. This enables researchers to analyze specific spectral features within a sample.
Property
Notch filters are selected based on their centre wavelength (the wavelength they block) and bandwidth (the range of wavelengths they block).
Careful selection and calibration of notch filters are crucial to achieving the desired spectral separation and noise reduction in biomedical imaging applications.
